Amazon AWS
Deploy VM
Deploy VyOS on Amazon AWS
Click to
InstancesandLaunch Instance

On the marketplace search “VyOS”
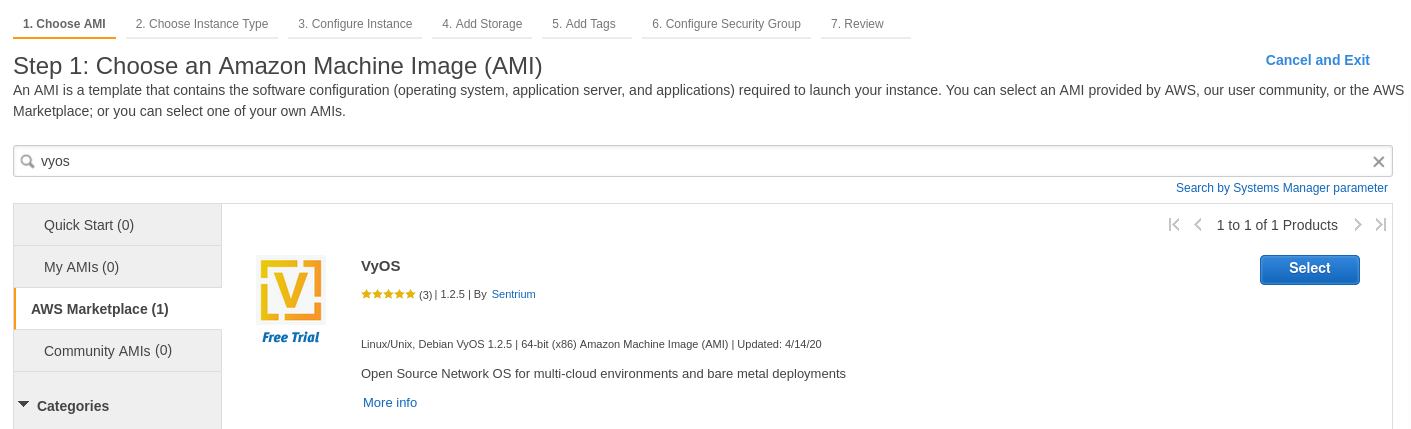
Choose the instance type. Minimum recommendation start from
m3.medium

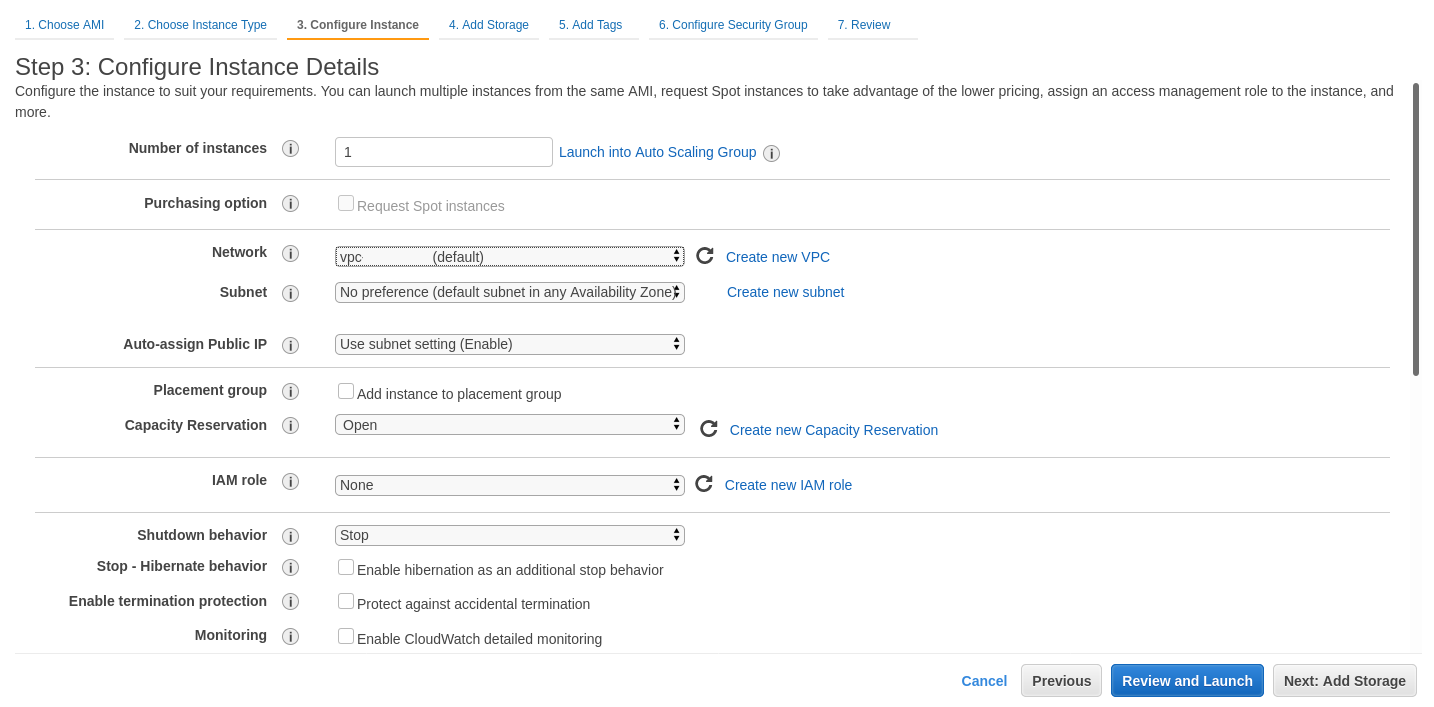
Configure instance for your requirements. Select number of instances / network / subnet
Additional storage. You can remove additional storage
/dev/sdb. First root device will be/dev/xvda. You can skip this step.

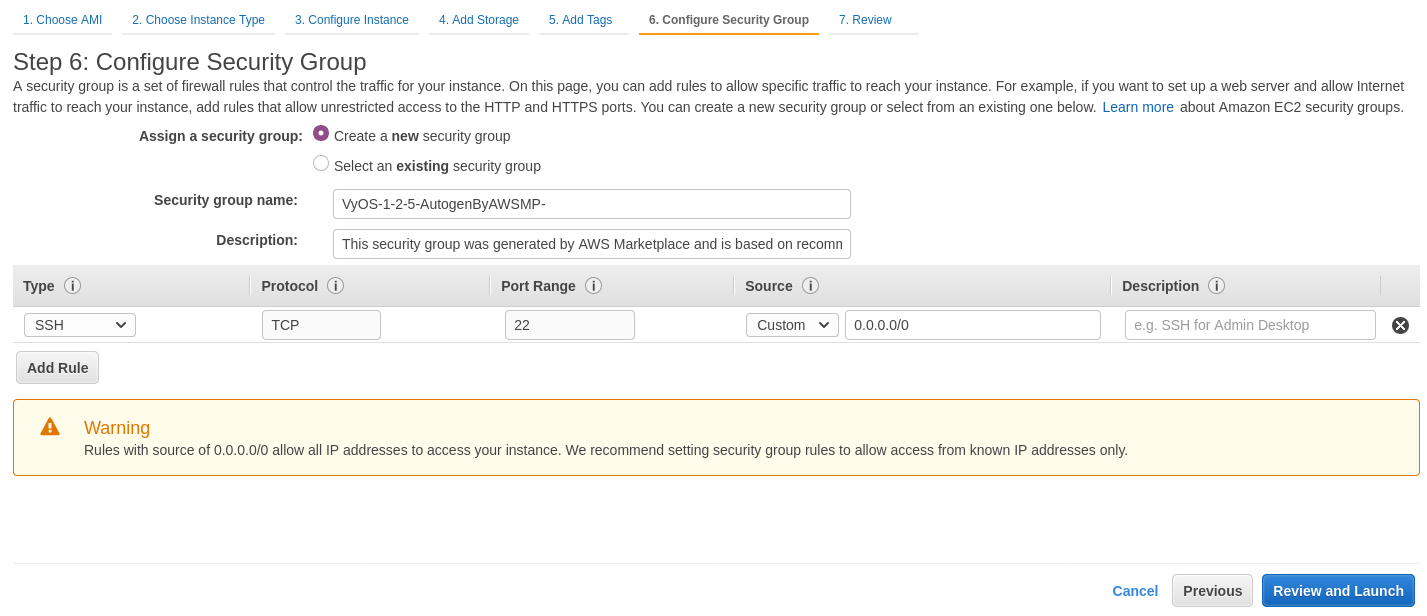
Configure Security Group. It’s recommended that you configure ssh access only from certain address sources. Or permit any (by default).
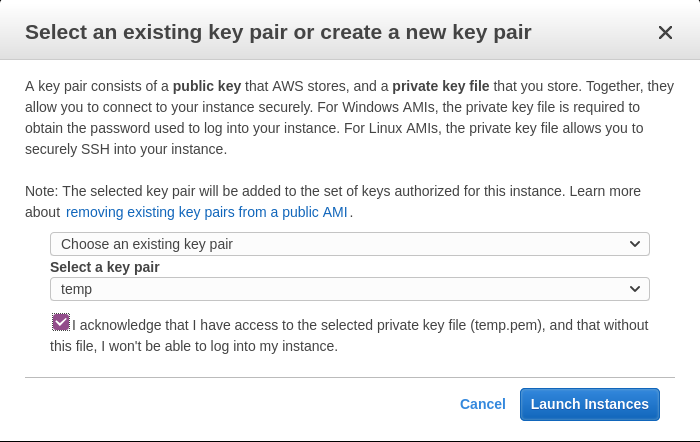
Select SSH key pair and click
Launch Instances
Find out your public IP address.

Connect to the instance by SSH key.
ssh -i ~/.ssh/amazon.pem [email protected] vyos@ip-192-0-2-10:~$
Amazon CloudWatch Agent Usage
To use Amazon CloudWatch Agent, configure it within the Amazon SSM Parameter Store. If you don’t have a configuration yet, do CloudWatch SSM Configuration creation.
Create an IAM role for the EC2 instance to access CloudWatch service, and name it CloudWatchAgentServerRole. The role should contain two default policies: CloudWatchAgentServerPolicy and AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore.
Attach the created role to your VyOS EC2 instance.
Ensure that amazon-cloudwatch-agent package is installed.
$ sudo apt list --installed | grep amazon-cloudwatch-agentNote
The amazon-cloudwatch-agent package is normally included in VyOS 1.3.3+ and 1.4+
Retrieve an existing CloudWatch Agent configuration from the SSM Parameter Store.
$ sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl -a fetch-config -m ec2 -s -c ssm:<your-configuration-name>This step also enables systemd service and runs it.
Note
The VyOS platform-specific scripts feature is under development. Thus, this step should be repeated manually after changing system image (Update VyOS)
CloudWatch SSM Configuration creation
Creating the Amazon Cloudwatch Agent Configuration in Amazon SSM Parameter Store.
Create an IAM role for your EC2 instance to access the CloudWatch service. Name it CloudWatchAgentAdminRole. The role should contain at two default policies: CloudWatchAgentAdminPolicy and AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore.
Note
CloudWatchAgentServerRole is too permissive and should be used for single configuration creation and deployment. That’s why after completion of step #3 highly recommended to replace instance CloudWatchAgentAdminRole role with CloudWatchAgentServerRole.
Run Cloudwatch configuration wizard.
$ sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-config-wizard
When prompted, answer “yes” to the question “Do you want to store the config in the SSM parameter store?”.