IPv4 Firewall Configuration
Overview
In this section there’s useful information of all firewall configuration that can be done regarding IPv4, and appropiate op-mode commands. Configuration commands covered in this section:
From main structure defined in Firewall Overview in this section you can find detailed information only for the next part of the general structure:
- set firewall
* ipv4
- forward
+ filter
- input
+ filter
- output
+ filter
- name
+ custom_name
For transit traffic, which is received by the router and forwarded, base chain is forward. A simplified packet flow diagram for transit traffic is shown next:
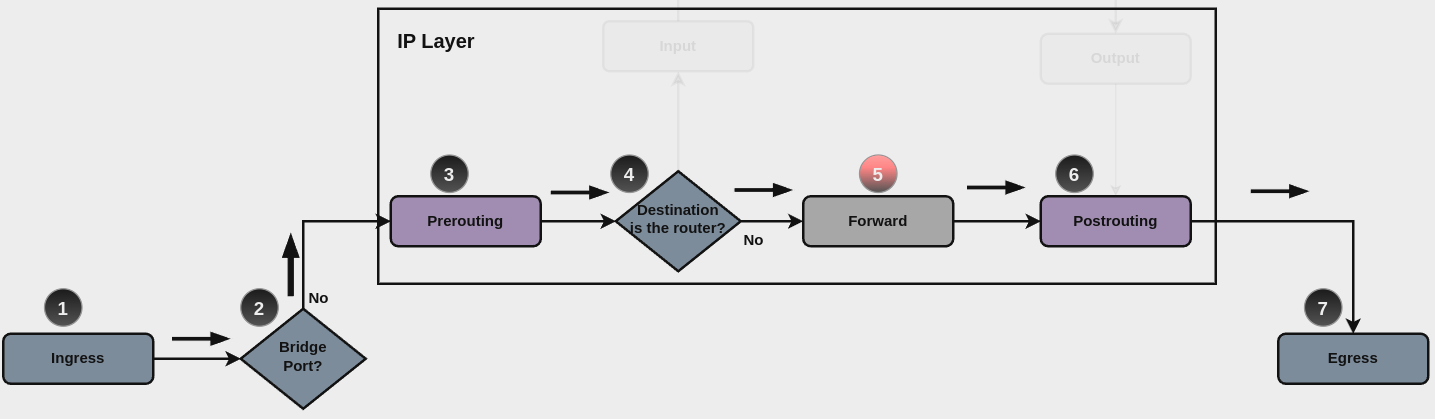
Where firewall base chain to configure firewall filtering rules for transit
traffic is set firewall ipv4 forward filter ..., which happens in stage 5,
highlightened with red color.
For traffic towards the router itself, base chain is input, while traffic originated by the router, base chain is output. A new simplified packet flow diagram is shown next, which shows the path for traffic destinated to the router itself, and traffic generated by the router (starting from circle number 6):
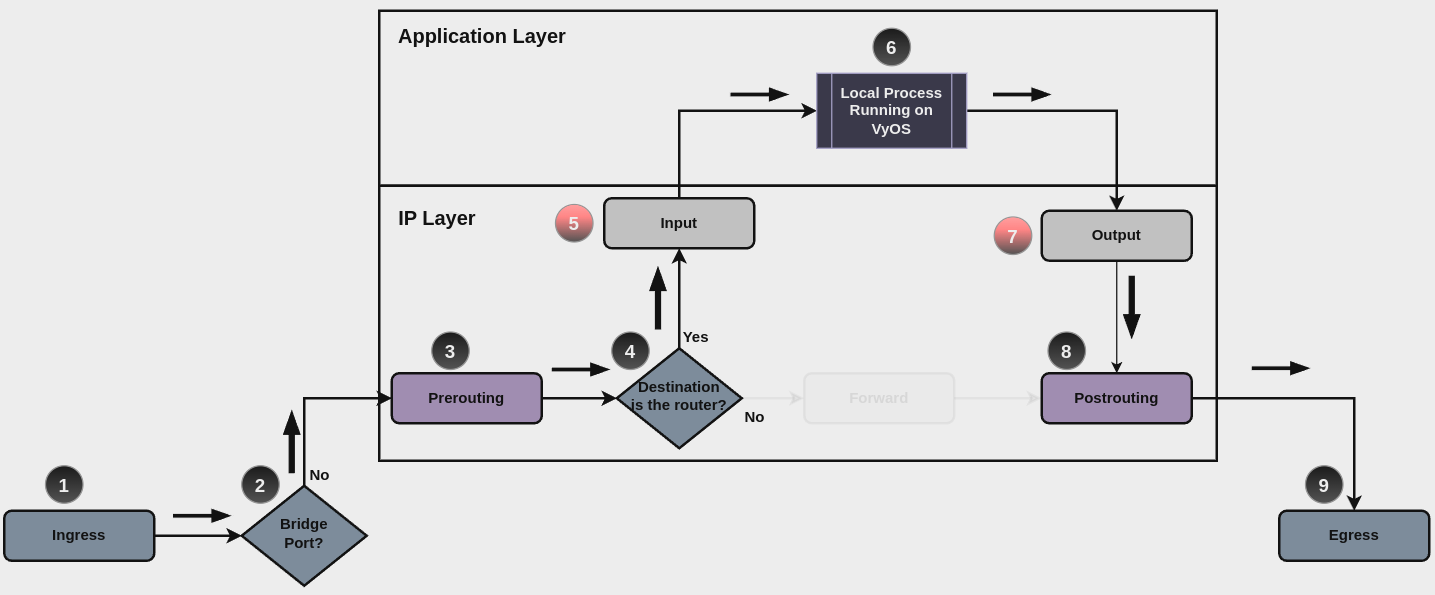
Base chain is for traffic toward the router is set firewall ipv4 input
filter ...
And base chain for traffic generated by the router is set firewall ipv4
output filter ...
Note
Important note about default-actions: If default action for any base chain is not defined, then the default action is set to accept for that chain. For custom chains, if default action is not defined, then the default-action is set to drop
Custom firewall chains can be created, with commands
set firewall ipv4 name <name> .... In order to use
such custom chain, a rule with action jump, and the appropiate target
should be defined in a base chain.
Firewall - IPv4 Rules
For firewall filtering, firewall rules needs to be created. Each rule is numbered, has an action to apply if the rule is matched, and the ability to specify multiple criteria matchers. Data packets go through the rules from 1 - 999999, so order is crucial. At the first match the action of the rule will be executed.
Actions
If a rule is defined, then an action must be defined for it. This tells the firewall what to do if all criteria matchers defined for such rule do match.
The action can be :
accept: accept the packet.
continue: continue parsing next rule.
drop: drop the packet.
reject: reject the packet.
jump: jump to another custom chain.
return: Return from the current chain and continue at the next rule of the last chain.
queue: Enqueue packet to userspace.
synproxy: synproxy the packet.
This required setting defines the action of the current rule. If action is set to jump, then jump-target is also needed.
To be used only when action is set to jump. Use this command to specify
jump target.
To be used only when action is set to queue. Use this command to specify
queue target to use. Queue range is also supported.
To be used only when action is set to queue. Use this command to let
packet go through firewall when no userspace software is connected to the
queue.
To be used only when action is set to queue. Use this command to
distribute packets between several queues.
Also, default-action is an action that takes place whenever a packet does not match any rule in it’s chain. For base chains, possible options for default-action are accept or drop.
This set the default action of the rule-set if no rule matched a packet
criteria. If default-action is set to jump, then
default-jump-target is also needed. Note that for base chains, default
action can only be set to accept or drop, while on custom chain,
more actions are available.
To be used only when defult-action is set to jump. Use this
command to specify jump target for default rule.
Note
Important note about default-actions: If default action for any base chain is not defined, then the default action is set to accept for that chain. For custom chains, if default action is not defined, then the default-action is set to drop.
Firewall Logs
Logging can be enable for every single firewall rule. If enabled, other log options can be defined.
Enable logging for the matched packet. If this configuration command is not present, then log is not enabled.
Use this command to enable the logging of the default action on the specified chain.
Define log-level. Only applicable if rule log is enable.
Define log group to send message to. Only applicable if rule log is enable.
Define length of packet payload to include in netlink message. Only applicable if rule log is enable and log group is defined.
Firewall Description
For reference, a description can be defined for every single rule, and for every defined custom chain.
Provide a rule-set description to a custom firewall chain.
Rule Status
When defining a rule, it is enable by default. In some cases, it is useful to just disable the rule, rather than removing it.
Matching criteria
There are a lot of matching criteria against which the packet can be tested.
Match criteria based on nat connection status.
Match criteria based on connection mark.
Match based on connection tracking protocol helper module to secure use of that helper module. See below for possible completions <module>.
Possible completions:
ftp Related traffic from FTP helper
h323 Related traffic from H.323 helper
pptp Related traffic from PPTP helper
nfs Related traffic from NFS helper
sip Related traffic from SIP helper
tftp Related traffic from TFTP helper
sqlnet Related traffic from SQLNet helper
Match criteria based on source and/or destination address. This is similar to the network groups part, but here you are able to negate the matching addresses.
set firewall ipv4 name FOO rule 50 source address 192.0.2.10-192.0.2.11
# with a '!' the rule match everything except the specified subnet
set firewall ipv4 input filter FOO rule 51 source address !203.0.113.0/24
An arbitrary netmask can be applied to mask addresses to only match against a specific portion.
This functions for both individual addresses and address groups.
# Match any IPv4 address with `11` as the 2nd octet and `13` as the forth octet
set firewall ipv4 name FOO rule 100 destination address 0.11.0.13
set firewall ipv4 name FOO rule 100 destination address-mask 0.255.0.255
Specify a Fully Qualified Domain Name as source/destination matcher. Ensure router is able to resolve such dns query.
Match IP addresses based on its geolocation. More info: geoip matching. Use inverse-match to match anything except the given country-codes.
Data is provided by DB-IP.com under CC-BY-4.0 license. Attribution required, permits redistribution so we can include a database in images(~3MB compressed). Includes cron script (manually callable by op-mode update geoip) to keep database and rules updated.
Only in the source criteria, you can specify a mac-address.
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 100 source mac-address 00:53:00:11:22:33
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 101 source mac-address !00:53:00:aa:12:34
A port can be set with a port number or a name which is here
defined: /etc/services.
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 10 source port '22'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 11 source port '!http'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 12 source port 'https'
Multiple source ports can be specified as a comma-separated list.
The whole list can also be “negated” using !. For example:
Use a specific address-group. Prepend character ! for inverted matching
criteria.
Use a specific network-group. Prepend character ! for inverted matching
criteria.
Use a specific port-group. Prepend character ! for inverted matching
criteria.
Use a specific domain-group. Prepend character ! for inverted matching
criteria.
Use a specific mac-group. Prepend character ! for inverted matching
criteria.
Match based on dscp value.
Match based on fragment criteria.
Match based on icmp code and type.
Match based on icmp type-name criteria. Use tab for information about what type-name criteria are supported.
Match based on inbound interface. Wilcard * can be used.
For example: eth2*. Prepending character ! for inverted matching
criteria is also supportd. For example !eth2
Match based on inbound interface group. Prepending character ! for
inverted matching criteria is also supportd. For example !IFACE_GROUP
Match based on outbound interface. Wilcard * can be used.
For example: eth2*. Prepending character ! for inverted matching
criteria is also supportd. For example !eth2
Match based on outbound interface group. Prepending character ! for
inverted matching criteria is also supportd. For example !IFACE_GROUP
Match based on ipsec criteria.
Match based on the maximum number of packets to allow in excess of rate.
Match based on the maximum average rate, specified as integer/unit. For example 5/minutes
Match based on packet length criteria. Multiple values from 1 to 65535 and ranges are supported.
Match based on packet type criteria.
Match a protocol criteria. A protocol number or a name which is here
defined: /etc/protocols.
Special names are all for all protocols and tcp_udp for tcp and udp
based packets. The ! negate the selected protocol.
set firewall ipv4 forward fitler rule 10 protocol tcp_udp
set firewall ipv4 forward fitler rule 11 protocol !tcp_udp
Match bases on recently seen sources.
Allowed values fpr TCP flags: ack, cwr, ecn, fin, psh,
rst, syn and urg. Multiple values are supported, and for
inverted selection use not, as shown in the example.
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 10 tcp flags 'ack'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 12 tcp flags 'syn'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 13 tcp flags not 'fin'
Match time to live parameter, where ‘eq’ stands for ‘equal’; ‘gt’ stands for ‘greater than’, and ‘lt’ stands for ‘less than’.
Synproxy
Synproxy connections
Set TCP-MSS (maximum segment size) for the connection
Set the window scale factor for TCP window scaling
Example synproxy
Requirements to enable synproxy:
Traffic must be symmetric
Synproxy relies on syncookies and TCP timestamps, ensure these are enabled
Disable conntrack loose track option
set system sysctl parameter net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps value '1'
set system conntrack tcp loose disable
set system conntrack ignore ipv4 rule 10 destination port '8080'
set system conntrack ignore ipv4 rule 10 protocol 'tcp'
set system conntrack ignore ipv4 rule 10 tcp flags syn
set firewall global-options syn-cookies 'enable'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 10 action 'synproxy'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 10 destination port '8080'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 10 inbound-interface interface-name 'eth1'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 10 protocol 'tcp'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 10 synproxy tcp mss '1460'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 10 synproxy tcp window-scale '7'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 1000 action 'drop'
set firewall ipv4 input filter rule 1000 state invalid 'enable'
Operation-mode Firewall
Rule-set overview
This will show you a basic firewall overview, for all ruleset, and not only for ipv4
vyos@vyos:~$ show firewall
Rulesets Information
---------------------------------
ipv4 Firewall "forward filter"
Rule Action Protocol Packets Bytes Conditions
------- -------- ---------- --------- ------- -----------------------------
20 accept all 0 0 ip saddr @N_TRUSTEDv4 accept
21 jump all 0 0 jump NAME_AUX
default accept all 0 0
---------------------------------
ipv4 Firewall "input filter"
Rule Action Protocol Packets Bytes Conditions
------- -------- ---------- --------- ------- -------------------------
10 accept all 156 14377 iifname != @I_LAN accept
default accept all 0 0
---------------------------------
ipv4 Firewall "name AUX"
Rule Action Protocol Packets Bytes Conditions
------ -------- ---------- --------- ------- --------------------------------------------
10 accept icmp 0 0 meta l4proto icmp accept
20 accept udp 0 0 meta l4proto udp ip saddr @A_SERVERS accept
30 drop all 0 0 ip saddr != @A_SERVERS iifname "eth2"
---------------------------------
ipv4 Firewall "output filter"
Rule Action Protocol Packets Bytes Conditions
------- -------- ---------- --------- ------- ----------------------------------------
10 reject all 0 0 oifname @I_LAN
20 accept icmp 2 168 meta l4proto icmp oifname "eth0" accept
default accept all 72 9258
---------------------------------
ipv6 Firewall "input filter"
Rule Action Protocol Packets Bytes Conditions
------- -------- ---------- --------- ------- -------------------------------
10 accept all 0 0 ip6 saddr @N6_TRUSTEDv6 accept
default accept all 2 112
vyos@vyos:~$
This will show you a summary of rule-sets and groups
vyos@vyos:~$ show firewall summary
Ruleset Summary
IPv6 Ruleset:
Ruleset Hook Ruleset Priority Description
-------------- -------------------- -------------------------
forward filter
input filter
ipv6_name IPV6-VyOS_MANAGEMENT
ipv6_name IPV6-WAN_IN PUBLIC_INTERNET
IPv4 Ruleset:
Ruleset Hook Ruleset Priority Description
-------------- ------------------ -------------------------
forward filter
input filter
name VyOS_MANAGEMENT
name WAN_IN PUBLIC_INTERNET
Firewall Groups
Name Type References Members
----------------------- ------------------ ----------------------- ----------------
PBX address_group WAN_IN-100 198.51.100.77
SERVERS address_group WAN_IN-110 192.0.2.10
WAN_IN-111 192.0.2.11
WAN_IN-112 192.0.2.12
WAN_IN-120
WAN_IN-121
WAN_IN-122
SUPPORT address_group VyOS_MANAGEMENT-20 192.168.1.2
WAN_IN-20
PHONE_VPN_SERVERS address_group WAN_IN-160 10.6.32.2
PINGABLE_ADRESSES address_group WAN_IN-170 192.168.5.2
WAN_IN-171
PBX ipv6_address_group IPV6-WAN_IN-100 2001:db8::1
SERVERS ipv6_address_group IPV6-WAN_IN-110 2001:db8::2
IPV6-WAN_IN-111 2001:db8::3
IPV6-WAN_IN-112 2001:db8::4
IPV6-WAN_IN-120
IPV6-WAN_IN-121
IPV6-WAN_IN-122
SUPPORT ipv6_address_group IPV6-VyOS_MANAGEMENT-20 2001:db8::5
IPV6-WAN_IN-20
This command will give an overview of a single rule-set.
vyos@vyos:~$ show firewall ipv4 input filter
Ruleset Information
---------------------------------
IPv4 Firewall "input filter"
Rule Action Protocol Packets Bytes Conditions
------- -------- ---------- --------- ------- -----------------------------------------
5 jump all 0 0 iifname "eth2" jump NAME_VyOS_MANAGEMENT
default accept all
This command will give an overview of a rule in a single rule-set, plus information for default action.
vyos@vyos:~$show firewall ipv4 output filter rule 20
Rule Information
---------------------------------
ipv4 Firewall "output filter"
Rule Action Protocol Packets Bytes Conditions
------- -------- ---------- --------- ------- ----------------------------------------
20 accept icmp 2 168 meta l4proto icmp oifname "eth0" accept
default accept all 286 47614
vyos@vyos:~$
Show Firewall log
Example Partial Config
firewall {
group {
network-group BAD-NETWORKS {
network 198.51.100.0/24
network 203.0.113.0/24
}
network-group GOOD-NETWORKS {
network 192.0.2.0/24
}
port-group BAD-PORTS {
port 65535
}
}
ipv4 {
forward {
filter {
default-action accept
rule 5 {
action accept
source {
group {
network-group GOOD-NETWORKS
}
}
}
rule 10 {
action drop
description "Bad Networks"
protocol all
source {
group {
network-group BAD-NETWORKS
}
}
}
}
}
}
}