Flowtables Firewall Configuration
Note
Documentation under development
Overview
In this section there’s useful information of all firewall configuration that can be done regarding flowtables.
From main structure defined in Firewall Overview in this section you can find detailed information only for the next part of the general structure:
- set firewall
* flowtable
- custom_flow_table
+ ...
Flowtables allows you to define a fastpath through the flowtable datapath. The flowtable supports for the layer 3 IPv4 and IPv6 and the layer 4 TCP and UDP protocols.
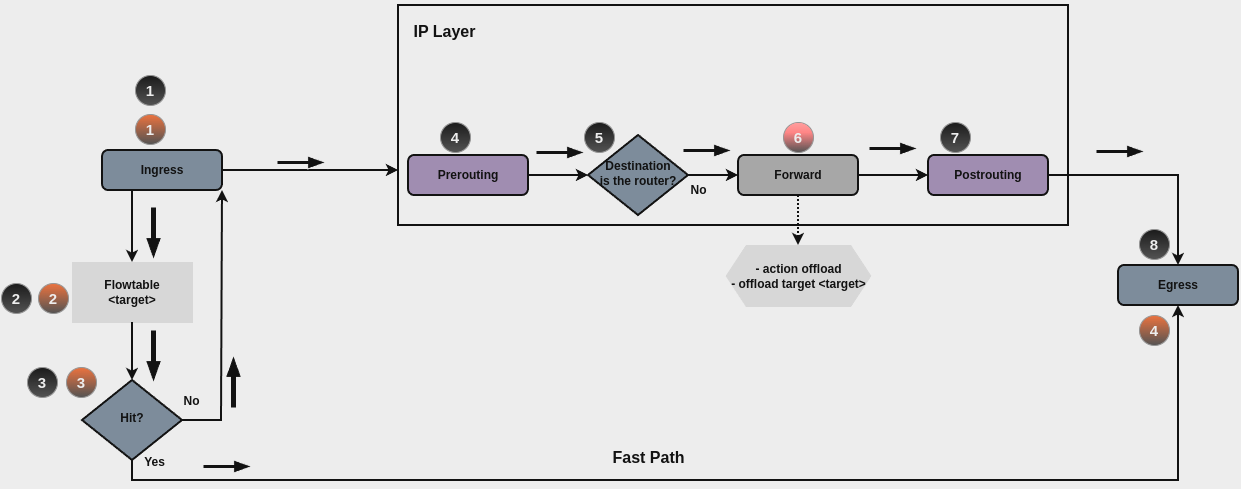
Once the first packet of the flow successfully goes through the IP forwarding path (black circles path), from the second packet on, you might decide to offload the flow to the flowtable through your ruleset. The flowtable infrastructure provides a rule action that allows you to specify when to add a flow to the flowtable (On forward filtering, red circle number 6)
A packet that finds a matching entry in the flowtable (flowtable hit) is transmitted to the output netdevice, hence, packets bypass the classic IP forwarding path and uses the Fast Path (orange circles path). The visible effect is that you do not see these packets from any of the Netfilter hooks coming after ingress. In case that there is no matching entry in the flowtable (flowtable miss), the packet follows the classic IP forwarding path.
Note
Flowtable Reference: https://docs.kernel.org/networking/nf_flowtable.html
Flowtable Configuration
In order to use flowtables, the minimal configuration needed includes:
Create flowtable: create flowtable, which includes the interfaces that are going to be used by the flowtable.
Create firewall rule: create a firewall rule, setting action to
offloadand using desired flowtable foroffload-target.
Creating a flow table:
Define interfaces to be used in the flowtable.
Provide a description to the flow table.
Define type of offload to be used by the flowtable: hardware or
software. By default, software offload is used.
Note
Hardware offload: should be supported by the NICs used.
Creating rules for using flow tables:
Create firewall rule in forward chain, and set action to offload.
Configuration Example
Things to be considred in this setup:
Two interfaces are going to be used in the flowtables: eth0 and eth1
Minumum firewall ruleset is provided, which includes some filtering rules, and appropiate rules for using flowtable offload capabilities.
As described, first packet will be evaluated by all the firewall path, so desired connection should be explicitely accepted. Same thing should be taken into account for traffic in reverse order. In most cases state policies are used in order to accept connection in reverse patch.
We will only accept traffic comming from interface eth0, protocol tcp and destination port 1122. All other traffic traspassing the router should be blocked.
Commands
set firewall flowtable FT01 interface 'eth0'
set firewall flowtable FT01 interface 'eth1'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter default-action 'drop'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 10 action 'offload'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 10 offload-target 'FT01'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 10 state 'established'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 10 state 'related'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 20 action 'accept'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 20 state 'established'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 20 state 'related'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 110 action 'accept'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 110 destination address '192.0.2.100'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 110 destination port '1122'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 110 inbound-interface name 'eth0'
set firewall ipv4 forward filter rule 110 protocol 'tcp'
Explanation
Analysis on what happens for desired connection:
1. First packet is received on eht0, with destination address 192.0.2.100, protocol tcp and destination port 1122. Assume such destination address is reachable through interface eth1.
2. Since this is the first packet, connection status of this connection, so far is new. So neither rule 10 nor 20 are valid.
Rule 110 is hit, so connection is accepted.
4. Once answer from server 192.0.2.100 is seen in opposite direction, connection state will be triggered to established, so this reply is accepted in rule 10.
5. Second packet for this connection is received by the router. Since connection state is established, then rule 10 is hit, and a new entry in the flowtable FT01 is added for this connection.
6. All subsecuent packets will skip traditional path, and will be offloaded and will use the Fast Path.
Checks
It’s time to check conntrack table, to see if any connection was accepted, and if was properly offloaded
vyos@FlowTables:~$ show firewall ipv4 forward filter
Ruleset Information
---------------------------------
ipv4 Firewall "forward filter"
Rule Action Protocol Packets Bytes Conditions
------- -------- ---------- --------- ------- ----------------------------------------------------------------
10 offload all 8 468 ct state { established, related } flow add @VYOS_FLOWTABLE_FT01
20 accept all 8 468 ct state { established, related } accept
110 accept tcp 2 120 ip daddr 192.0.2.100 tcp dport 1122 iifname "eth0" accept
default drop all 7 420
vyos@FlowTables:~$ sudo conntrack -L | grep tcp
conntrack v1.4.6 (conntrack-tools): 5 flow entries have been shown.
tcp 6 src=198.51.100.100 dst=192.0.2.100 sport=41676 dport=1122 src=192.0.2.100 dst=198.51.100.100 sport=1122 dport=41676 [OFFLOAD] mark=0 use=2
vyos@FlowTables:~$