Multicast
VyOS facilitates IP Multicast by supporting PIM Sparse Mode, IGMP and IGMP-Proxy.
PIM and IGMP
PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) must be configured in every interface of every participating router. Every router must also have the location of the Rendevouz Point manually configured. Then, unidirectional shared trees rooted at the Rendevouz Point will automatically be built for multicast distribution.
Traffic from multicast sources will go to the Rendezvous Point, and receivers will pull it from a shared tree using IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol).
Multicast receivers will talk IGMP to their local router, so, besides having PIM configured in every router, IGMP must also be configured in any router where there could be a multicast receiver locally connected.
VyOS supports both IGMP version 2 and version 3 (which allows source-specific multicast).
Example
In the following example we can see a basic multicast setup:
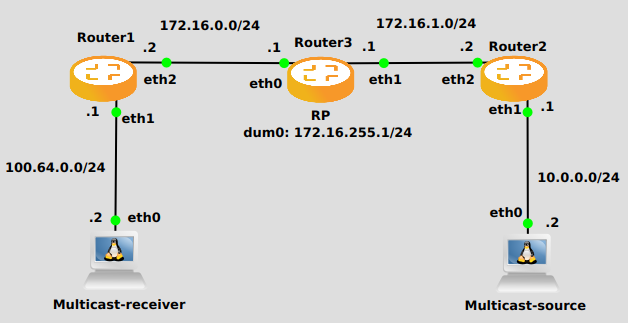
Router 1
set interfaces ethernet eth2 address '172.16.0.2/24'
set interfaces ethernet eth1 address '100.64.0.1/24'
set protocols ospf area 0 network '172.16.0.0/24'
set protocols ospf area 0 network '100.64.0.0/24'
set protocols igmp interface eth1
set protocols pim interface eth1
set protocols pim interface eth2
set protocols pim rp address 172.16.255.1 group '224.0.0.0/4'
Router 3
set interfaces dummy dum0 address '172.16.255.1/24'
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address '172.16.0.1/24'
set interfaces ethernet eth1 address '172.16.1.1/24'
set protocols ospf area 0 network '172.16.0.0/24'
set protocols ospf area 0 network '172.16.255.0/24'
set protocols ospf area 0 network '172.16.1.0/24'
set protocols pim interface dum0
set protocols pim interface eth0
set protocols pim interface eth1
set protocols pim rp address 172.16.255.1 group '224.0.0.0/4'
Router 2
set interfaces ethernet eth1 address '10.0.0.1/24'
set interfaces ethernet eth2 address '172.16.1.2/24'
set protocols ospf area 0 network '10.0.0.0/24'
set protocols ospf area 0 network '172.16.1.0/24'
set protocols pim interface eth1
set protocols pim interface eth2
set protocols pim rp address 172.16.255.1 group '224.0.0.0/4'
Basic commands
These are the commands for a basic setup.
Use this command to enable PIM in the selected interface so that it can communicate with PIM neighbors.
Use this command to manually configure a Rendezvous Point for PIM so that join messages can be sent there. Set the Rendevouz Point address and the matching prefix of group ranges covered. These values must be shared with every router participating in the PIM network.
Tuning commands
You can also tune multicast with the following commands.
Use this PIM command in the selected interface to set the priority (1-4294967295) you want to influence in the election of a node to become the Designated Router for a LAN segment. The default priority is 1, set a higher value to give the router more preference in the DR election process.
Use this command to configure the PIM hello interval in seconds (1-180) for the selected interface.
Use this PIM command to modify the time out value (31-60000 seconds) for an (S,G) flow. 31 seconds is chosen for a lower bound as some hardware platforms cannot see data flowing in better than 30 seconds chunks.
Use this command to allow the selected interface to join a multicast group defining the multicast address you want to join and the source IP address too.
Use this command to configure in the selected interface the IGMP host query interval (1-1800) in seconds that PIM will use.
Use this command to configure in the selected interface the IGMP query response timeout value (10-250) in deciseconds. If a report is not returned in the specified time, it will be assumed the (S,G) or (*,G) state has timed out.
IGMP Proxy
IGMP proxy sends IGMP host messages on behalf of a connected client. The configuration must define one, and only one upstream interface, and one or more downstream interfaces.
Configuration
upstream: The upstream network interface is the outgoing interface which is responsible for communicating to available multicast data sources. There can only be one upstream interface.
downstream: Downstream network interfaces are the distribution interfaces to the destination networks, where multicast clients can join groups and receive multicast data. One or more downstream interfaces must be configured.
Defines alternate sources for multicasting and IGMP data. The network address must be on the following format ‘a.b.c.d/n’. By default, the router will accept data from sources on the same network as configured on an interface. If the multicast source lies on a remote network, one must define from where traffic should be accepted.
This is especially useful for the upstream interface, since the source for multicast traffic is often from a remote location.
This option can be supplied multiple times.
Disables quickleave mode. In this mode the daemon will not send a Leave IGMP message upstream as soon as it receives a Leave message for any downstream interface. The daemon will not ask for Membership reports on the downstream interfaces, and if a report is received the group is not joined again the upstream.
If it’s vital that the daemon should act exactly like a real multicast client on the upstream interface, this function should be enabled.
Enabling this function increases the risk of bandwidth saturation.
Example
Interface eth1 LAN is behind NAT. In order to subscribe 10.0.0.0/23 subnet multicast which is in eth0 WAN we need to configure igmp-proxy.
set protocols igmp-proxy interface eth0 role upstream
set protocols igmp-proxy interface eth0 alt-subnet 10.0.0.0/23
set protocols igmp-proxy interface eth1 role downstream